Problem identified. Solution required. Time to execute
Athletes foot affects millions. You want facts. You want results. You want this sorted efficiently without drama or delay. This guide delivers exactly that.
No fluff. No emotional journey narratives. No gentle wellness chats. Just proven strategies, actionable steps, and measurable outcomes. Read. Implement. Resolve.
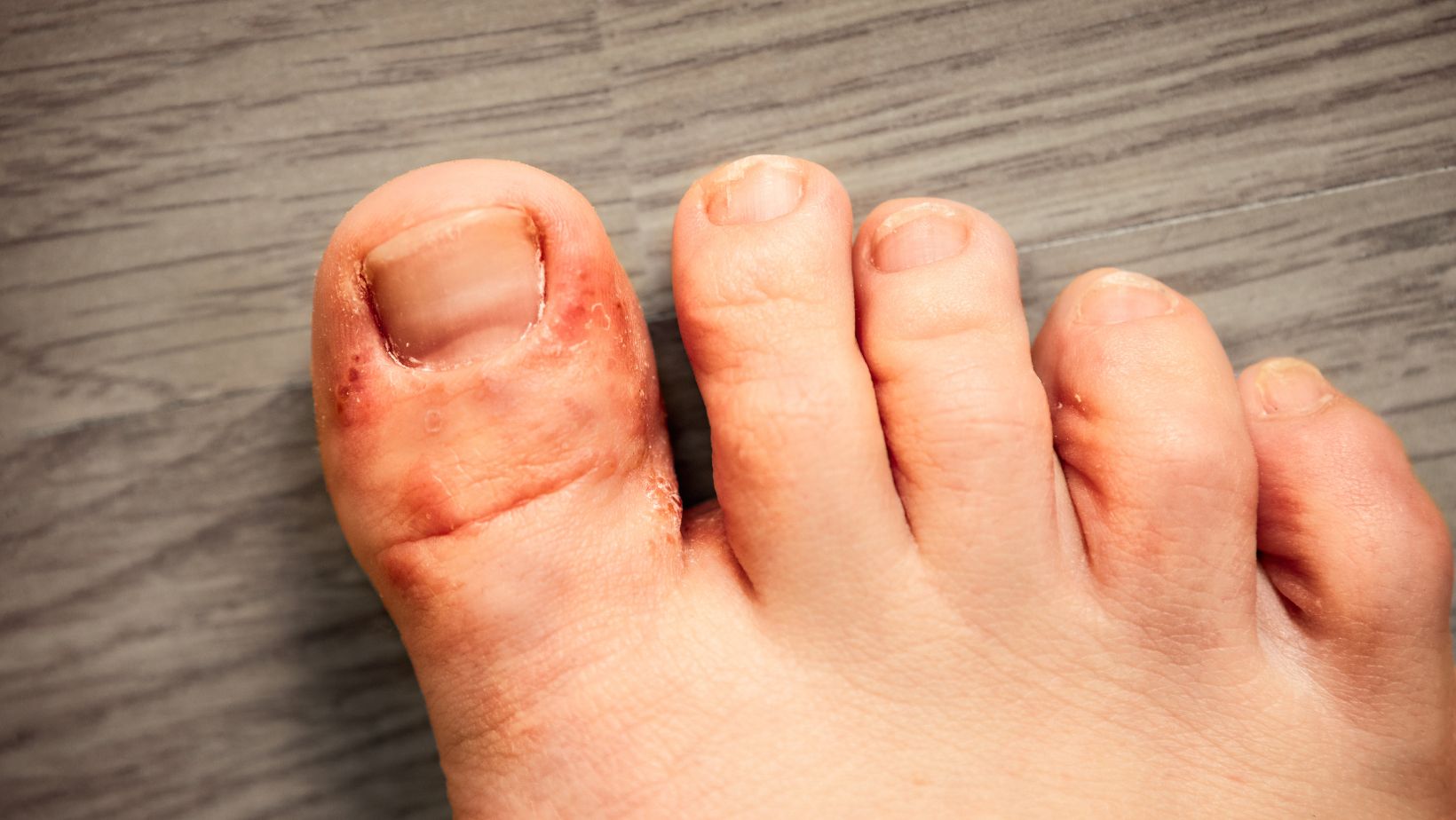
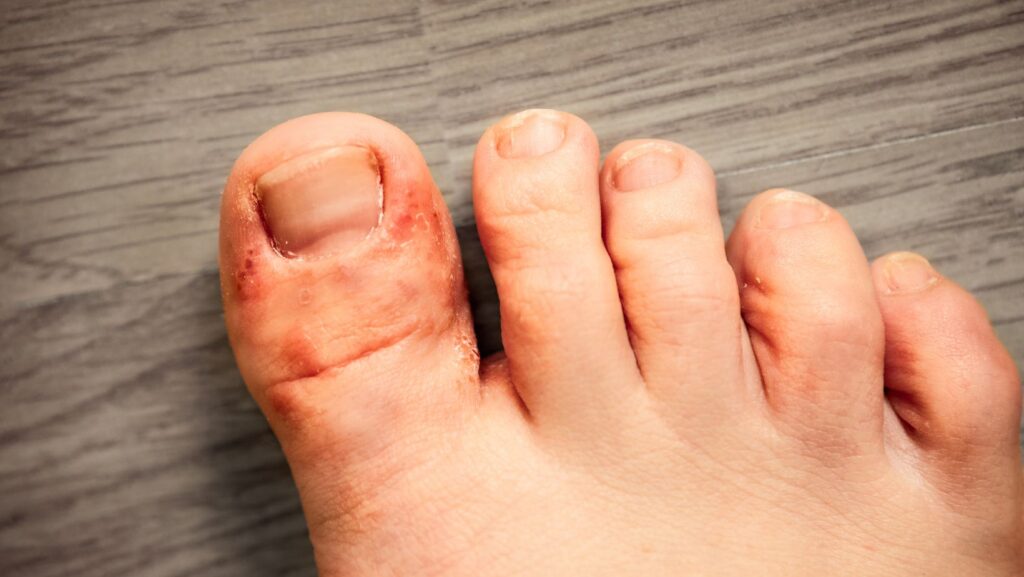
Athletes foot is a dermatophyte infection. Three main culprits exist. Treatment options are numerous. Success rates are high when protocols are followed correctly. Failure occurs when people deviate from proven methods or quit too early.
This condition costs the healthcare system billions annually. Individual cases cost time, money, and productivity. Prevention costs pennies. Treatment takes days to weeks when done properly. Recurrence is preventable with systematic approach.
You have options. Some work better than others. Some work faster than others. Some cost more than others. Data drives decisions. Results matter. Everything else is noise.
What You Are Dealing With
Trichophyton rubrum. Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Epidermophyton floccosum. These three organisms cause 90% of athletes foot cases. They consume keratin. They reproduce rapidly in warm, moist conditions. They create spores that survive for months.
Basic biology. Fungi need food, warmth, moisture. Your feet provide all three between the toes. Perfect breeding ground. Temperature 25-30°C. Humidity above 70%. Dead skin cells for nutrition. Recipe for infection.
Transmission occurs through direct contact or contaminated surfaces. Swimming pools, locker rooms, shared towels, infected footwear. Spores transfer easily. Infection establishes within 24-72 hours under optimal conditions.
Incubation period varies. Symptoms appear 1-3 weeks post-exposure typically. Some people show symptoms within days. Others remain asymptomatic for weeks. Individual immune response determines timeline.
Risk factors are quantifiable. Age 20-40 highest incidence. Males affected 2:1 ratio versus females. Athletes show 15-70% prevalence depending on sport. Diabetes increases risk 3x. Immunocompromised individuals show 5x higher rates.
Infection spreads predictably. Starts interdigitally. Moves to plantar surface. Can affect dorsal foot. May spread to hands via autoinoculation. Nail involvement occurs in 20% of chronic cases.
Three clinical presentations exist. Interdigital most common. Chronic plantar hyperkeratotic second most frequent. Acute vesicular least common but most symptomatic.
Diagnosis is straightforward. Clinical appearance plus KOH test confirms 95% of cases. Fungal culture takes 2-4 weeks but unnecessary in typical presentations. Wood’s lamp examination shows no fluorescence with dermatophytes.
Symptom Recognition Matrix
Primary symptoms appear in predictable sequence
Week 1. Mild itching between 4th and 5th toes. Intensifies after shoe removal. Scaling minimal. Visible changes subtle.
Week 2. Itching spreads to 3rd and 4th toe space. Skin appears white and soggy. Fine scaling develops. Mild odour possible.
Week 3. Scaling increases. Small fissures appear. Itching becomes constant. Burning sensation develops. Skin begins peeling.
Week 4 plus. Thick scaling. Deep fissures. Possible secondary bacterial infection. Extension to plantar surface. Nail involvement possible.
Vesicular type presents differently. Sudden onset. Fluid-filled blisters. Intense itching. Usually spring/summer occurrence. Resolution within 2-3 weeks if treated promptly.
Chronic hyperkeratotic type shows gradual onset. Dry scaling. Minimal itching. Resembles dry skin. Often misdiagnosed initially. Requires extended treatment.
Secondary bacterial infection indicators. Increased erythema. Warmth. Purulent discharge. Lymphangitis. Fever. Requires immediate medical attention.
Differential diagnosis considerations. Contact dermatitis from footwear. Psoriasis. Eczema. Bacterial infections. Erythrasma. Proper diagnosis prevents treatment delays.
Self-assessment accuracy is high. 85% of self-diagnosed cases prove correct. However, 15% represent other conditions requiring different treatment. When in doubt, seek professional confirmation.
Treatment Protocol Matrix
Topical antifungals show varying efficacy rates
Terbinafine cream. 80-90% cure rate. 7-14 day treatment. Fungicidal action. Continues working post-treatment. Most cost-effective option per cure.

Clotrimazole cream. 70-80% cure rate. 14-28 day treatment. Fungistatic action. Requires longer application. Lower cost per unit.
Miconazole cream. 75-85% cure rate. 14-21 day treatment. Broad spectrum. Good for mixed infections. Mid-range pricing.
Tolnaftate preparations. 60-70% cure rate. 14-28 day treatment. Excellent safety profile. Lower efficacy. Budget option.
Application protocol matters. Clean feet thoroughly. Dry completely. Apply thin layer. Extend 2cm beyond visible infection. Continue 1 week post-symptom resolution. Twice daily application standard.
Prescription options for resistant cases
Oral terbinafine. 95% cure rate. 2-6 week course. Systemic action. Higher cost. Requires monitoring. Reserved for extensive or resistant infections.
Prescription topicals. Ciclopirox, econazole, oxiconazole. 85-95% cure rates. Shorter treatment courses. Higher concentration active ingredients. Professional strength athlete’s foot powder formulations for complex cases like this offering from The Feets work effectively with prescription guidance.
Combination therapy for severe cases. Oral plus topical antifungals. Addresses systemic and local factors. 98% cure rate. Used for immunocompromised patients or extensive infections.
Treatment failure analysis. Incorrect diagnosis 30%. Inadequate treatment duration 40%. Reinfection from contaminated items 20%. Drug resistance 10%.
Natural Treatment Data
Tea tree oil studies show moderate efficacy
Concentration matters. 10% solutions show antifungal activity. 25-50% solutions more effective but increase irritation risk. Pure oil causes contact dermatitis in 15% of users.
Clinical trial results. 10% tea tree oil versus placebo. 68% improvement versus 25% placebo response. 25% tea tree oil versus terbinafine 1%. Comparable results but higher irritation rates.
Application protocol. Dilute to 10% concentration. Apply twice daily. Continue 4-6 weeks. Monitor for skin irritation. Discontinue if reactions occur.
Vinegar foot soaks show limited evidence
Mechanism. Acidic pH inhibits fungal growth. Acetic acid at 5% concentration shows antifungal properties in laboratory studies. Human trials limited.
Protocol. 1 part vinegar to 2 parts water. 15-20 minute soaks daily. White vinegar or apple cider vinegar. Continue 2-4 weeks.
Effectiveness data. Anecdotal reports positive. Controlled trials lacking. May help as adjunct therapy. Insufficient evidence as monotherapy.
Garlic preparations show promise
Active compound. Allicin demonstrates antifungal activity. Fresh garlic contains highest concentrations. Processing reduces potency.
Application method. Crush fresh cloves. Mix with carrier oil. Apply 30 minutes daily. Risk of contact dermatitis. Patch test recommended.
Clinical data limited. Laboratory studies promising. Human trials insufficient. Potential adjunct treatment only.
Prevention Strategy Implementation
Environmental control reduces reinfection risk by 80%.
Footwear management. Rotate shoes daily. Use antifungal sprays. Replace heavily contaminated items. Choose breathable materials. Avoid synthetic materials when possible.
Sock selection criteria. Moisture-wicking materials. Change when damp. Wash in hot water 60°C+. Antimicrobial treatments optional. Cotton avoided for active individuals.
Hygiene protocols. Daily foot washing mandatory. Thorough drying essential. Separate foot towels recommended. Hot water laundering for towels and socks.
Environmental decontamination. Clean shower floors weekly. Disinfect communal areas. UV treatment for shoes optional. Replace contaminated nail tools.
High-risk environment protection. Public pools require protective footwear. Gym showers never barefoot. Hotel rooms inspect carefully. Shared accommodation extra precautions.
Personal risk factor modification. Blood glucose control for diabetics. Immune system support. Stress reduction. Adequate sleep. Proper nutrition.
Family transmission prevention. Avoid sharing towels. Separate washcloths. Individual nail tools. Immediate treatment of infected members.
Professional Intervention Triggers
Seek immediate medical care when specific criteria met.
Treatment failure indicators. No improvement after 2 weeks proper treatment. Worsening symptoms despite treatment. Recurrence within 3 months of treatment.
Complication signs. Red streaking from infection site. Increased warmth and swelling. Purulent discharge. Fever development. Lymph node enlargement.
High-risk patient categories. Diabetes mellitus. Immunocompromised status. Peripheral vascular disease. Age over 65. Previous complications.
Extensive infection criteria. Involvement of both feet. Spread to hands or nails. Coverage exceeding 25% of foot surface. Chronic hyperkeratotic type.
Diagnostic uncertainty situations. Atypical presentation. Failed response to appropriate treatment. Recurrent infections. Concurrent skin conditions.
Prescription treatment options available. Oral antifungals for systemic treatment. Higher concentration topicals. Combination therapies. Specialised formulations.
Professional monitoring benefits. Treatment response assessment. Side effect monitoring. Drug interaction checking. Resistance testing when indicated.
Cost-effectiveness analysis shows early professional intervention reduces total treatment costs by 40% for high-risk patients.
Long Term Management Systems
Maintenance protocols prevent recurrence in 85% of cases.
Daily maintenance routine. Foot inspection 30 seconds. Antifungal powder application. Moisture control measures. Sock changes as needed.
Weekly protocols. Shoe rotation verification. Deep cleaning of frequently used footwear. Nail trimming with clean tools. Foot care equipment maintenance.
Monthly assessments. Foot health evaluation. Risk factor review. Product effectiveness assessment. Protocol adjustments as needed.
Seasonal adjustments required. Summer increases moisture control needs. Winter boot protocols different. Travel requires portable prevention kit. Activity-specific modifications.
Equipment replacement schedule. Athletic shoes every 300-500 miles. Casual shoes when sole wear visible. Socks when elastic fails. Nail tools annually minimum.
Risk situation protocols. Public facility visits require protective measures. Illness increases vigilance needs. Stress periods need enhanced care. Travel situations demand preparation.
Documentation value. Symptom tracking identifies patterns. Treatment response records guide future decisions. Trigger identification prevents recurrence. Cost tracking demonstrates ROI.
Success metrics. Zero recurrence 12 months post-treatment. Maintained daily protocols 90% compliance. No secondary complications. Cost under £50 annually.
Technology integration options. Smartphone reminders for protocols. UV shoe sanitisers for equipment. Moisture-monitoring socks available. Apps for symptom tracking.
Quality of life improvements measurable. Reduced anxiety about foot problems. Increased confidence in social situations. Improved sleep from reduced itching. Enhanced activity participation.
Prevention cost analysis. Daily prevention costs £0.50. Treatment episode costs £15-50. Prescription treatment costs £30-100. Professional consultation costs £50-150. Complications cost £200+.
Return on investment clear. Prevention investment of £180 annually prevents treatment costs of £500-1000. Time savings significant. Quality of life improvements quantifiable.
Success requires system thinking. Individual components work synergistically. Consistency matters more than perfection. Data drives continuous improvement. Results speak louder than intentions.
Implementation starts immediately. Delay increases costs. Procrastination enables progression. Action creates momentum. Results build motivation.
Your choice. Continue current path and accept recurring problems. Or implement systematic approach and achieve lasting results. Evidence supports the systematic approach. Data proves effectiveness. Success is achievable.
Execute the plan. Measure the results. Adjust as needed. Maintain the system. Enjoy healthy feet.
Bob Duncan is the lead writer and partner on ConversationsWithBianca.com. A passionate parent, he’s always excited to dive into the conversation about anything from parenting, food & drink, travel, to gifts & more!